July 25, 2022
You’ve found an item you want to buy online. At the checkout, you choose to use a payment service, such as PayPal. You enter your password – it takes a few tries, but you get there in the end. You’re then asked to type in the SMS one-time passcode sent to your smartphone. Your device is charging in another room so you go and get it and retrieve the code. The code is accepted and you complete the purchase.
This is an example of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Multi-factor authentication refers to a security process that uses multiple methods of authentication – in this case, a password and a one-time passcode sent to a smartphone – to verify a user’s identity. Multi-factor authentication regulations are a welcome defense against the growing threat of online fraud.
But as we saw in the example above, multi-factor authentication can cause friction. If you don’t have your smartphone handy, or you don’t have cellular access, MFA that uses OTPs can become an inconvenient roadblock for users and a conversion killer for organizations. Additionally, many MFA solutions lack inclusivity; switching between different devices and applications can be difficult for people with certain disabilities, or for those with inconsistent cell phone service.
The truth is that multi-factor authentication is only as secure, convenient, and inclusive as the technologies used to facilitate it. In this article, we’ll explain why biometric authentication is the more secure, convenient, and inclusive authentication factor – and why every MFA solution should take advantage of it.
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-factor authentication is an authentication process that requires the user to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a (secured) service or to complete a transaction. This could include accessing an online account or computer application, or authorizing a payment.
Multi-factor authentication aims to verify that you are who you say you are. MFA guidelines require a combination of two or more separate authentication factors. The authentication categories are:
- Something the user knows (knowledge-based authentication, like a password).
- Something the user has (possession-based authentication, like an SMS OTP sent to a device owned by the user).
- Something the user is (inherence-based authentication, like iProov biometric face authentication).
Any combination of the above is acceptable, but not two from the same category.
Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
More and more people are signing up for digital services online – for example, 27% of British adults have opened an account with an online-only bank (that’s 14 million people) – and they all expect a seamless user journey. But at the same time, fraud is on the rise and organizations must be vigilant.
Digital fraud is a very real threat and is growing more sophisticated by the day. For example, account takeover fraud (ATO) is a widespread problem. ATO fraudsters gain unauthorized access to a genuine user’s account, usually for financial gain — often making use of techniques such as credential stuffing to scale these attacks. You can read more on account takeover fraud here.
Additionally, a majority of today’s interactions happen remotely, operating from different locations, through unsecured networks, over untrusted hardware. So how do you ensure that the physical person is bound to their digital selves in a trusted, secure way?
Multi-factor authentication seeks to establish trust online under these hostile conditions and limit fraud through stronger authentication. The key is to establish trust and security without ever inconveniencing the user. Unfortunately, organizations don’t always get it right.
What Are the Risks of Multi-Factor Authentication?
The biggest risk with MFA is that it will cause a negative impact on the user experience. Every step in an online user journey is a potential opportunity for friction and drop-off. Each added step is also a potential issue for inclusion, as it increases the cognitive demands on the user.
This is a significant problem for organizations. Shoppers are inclined to abandon transactions if it takes too long to check out (as we’ll all likely know from first-hand experience!). And that’s assuming that the MFA process doesn’t abandon the transaction for them – Barclaycard research found that in February 2022 alone, more than 1.2m online transactions worth more than £100m were declined during the authentication process. Retailers lost sales as a result. About 14% of shoppers noticed an increase in their online payments being declined and 37% headed to another retailer to complete their purchase.
But higher security does not have to mean low usability (and vice versa). The best way to deliver enhanced security with high usability is passive biometric face verification – which is an iProov-specific biometric advantage.
We’ve written extensively about the risks and drawbacks of other authentication methods. You can read more on this below:
- Forgotten Passwords are Increasing Your Website’s Abandonment Rate
- One-Time Passcode (OTP) Authentication: What Are the Risks?
- Authentication Methods: What Is the Best Type of Authentication? (5 Types)
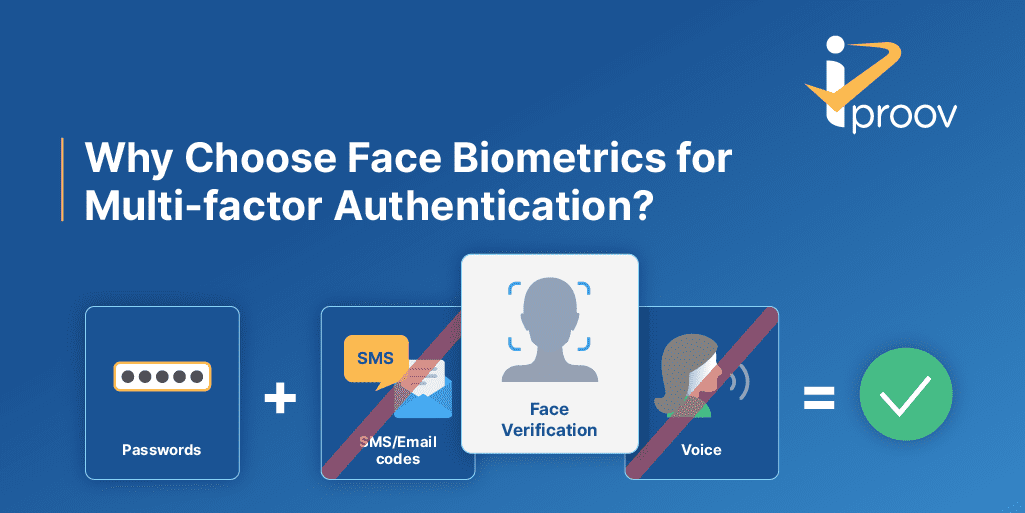
Why Are Biometrics the Solution for Multi-Factor Authentication?
Of the three types of authentication mentioned above – knowledge (e.g. passwords), possession (e.g. a mobile device) and inherence (e.g. face biometric authentication) – biometrics is the most secure and the most usable.
Biometrics is secure because it’s the only authentication factor that enables organizations to be certain that a physical person at the end of an internet connection is really who they claim to be. A password or a device can be shared or stolen, which means anyone could be using them. But nobody can take your physical face. Biometric face authentication ensures you’re dealing with the right person.
Biometrics is more usable because you always have your face with you. You can’t forget it (as with a password) or leave it at home or in another room (as with a device). And if you implement passive biometrics, then you can make the process as effortless as possible for your users.
Why Is Liveness Needed for Biometric Multi-Factor Authentication?
Liveness detection is part of biometric verification. It ensures that an online user is a real person, detecting if the face being presented to the camera is a live human being. Without liveness technology, criminals could spoof the authentication process with masks, photographs, and other presentation attacks. With liveness detection, no one can use a copy (i.e. a picture) of your face to access your account, because that picture would not pass a liveness assessment.
As we’ve established, choosing the biometric factor – ‘something you are’ – has many advantages for multi-factor authentication. But not all liveness is the same, and there are various solutions that deliver varying levels of assurance. That’s why you must ensure you’re choosing the right biometric vendor.
Why Should You Choose iProov Biometric Authentication as Part of Your Multi-Factor Authentication Strategy?
The best MFA solutions are those where the user is not expected to do anything. These are known as passive authentication. With iProov, the user knows that a secure process is taking place and they feel reassured by it, but the experience is effortless.
iProov’s biometric face verification is patented, proven at scale, and truly unique. iProov technology is essential to a successful MFA strategy because it proves that someone is the correct and genuine live human without the user having to do anything – the technology takes care of the authentication process.
Unlike with the MFA example in our intro, there’s no switching between devices or applications. It’s as simple as staring into the device’s user-facing camera. Ultimately, no action from the user is required.
iProov offers two options for MFA. Our Express Liveness technology asks a user to complete a brief face scan to confirm they are the right person and a real person. Our Dynamic Liveness technology also uses a brief face scan and delivers additional security by verifying that a user is the right and real person, but that they are also authenticating right now.
Both iProov technologies have been built to strike the balance between security and usability, enabling safety and trust without negatively impacting the customer experience.
Benefits of Using Biometric Multi-Factor Authentication
A number of factors combine to make iProov biometric authentication the perfect MFA solution:
- Inclusivity: Multi-factor authentication must be inclusive for as much of the population as possible to be successful. Crucially, iProov’s solution does not require reading or comprehending complex instructions — you simply look at your device’s user-facing camera. This means users can verify themselves easily, improving accessibility for those with various cognitive abilities. Additionally, iProov works on any device with a user-facing camera and is one of the first biometric vendors to achieve WCAG 2.1 AA conformance.
- Convenience: If multi-factor authentication isn’t easy to use, people won’t use it and will be more likely to abandon the process. iProov’s technology maximizes convenience; the user looks at their device, the device looks back, and the process is completed in a matter of seconds.
- Security: The key objective of MFA is strong authentication and iProov technology is used by the world’s most security-conscious organizations, such the Department of Homeland Security. Our cloud-based technology verifies that each person is the right person, a real person, and that they are authenticating right now – thwarting impostors and fraudsters from spoofing the system. iProov enables remote verification from anywhere and does not rely on the user’s device for security, removing the risk of a compromised device or camera. In the case of Dynamic Liveness, iProov defenses evolve with the changing threat landscape through the iProov Security Operations Center ( iSOC).
- Accessibility: iProov is device and platform-agnostic. There is no need for special hardware or sensors, as individuals can authenticate using any device with a user-facing camera. This includes smartphones, laptops, desktops, and tablets.
- Proven experience: With large-scale solution deployments around the world, iProov can offer the necessary expertise, technology, and knowledge to support critical MFA implementations – view our case studies here.
Multi-Factor Authentication Using Biometrics: A Summary
- Multi-factor authentication refers to an authentication process that requires the user to provide two or more factors to access an online service.
- Some MFA methods – such as OTPs – can lead to users abandoning transactions.
- iProov biometric authentication with liveness detection is the most secure, usable and inclusive factor for MFA.
- iProov’s Express Liveness and Dynamic Liveness technologies provide organizations with the appropriate level of security for all MFA scenarios.
If you’d like to learn more, you can visit our multi-factor authentication page or book an iProov demo here.
Or, want to brush up on your biometric knowledge? Visit our Biometric Encyclopedia!